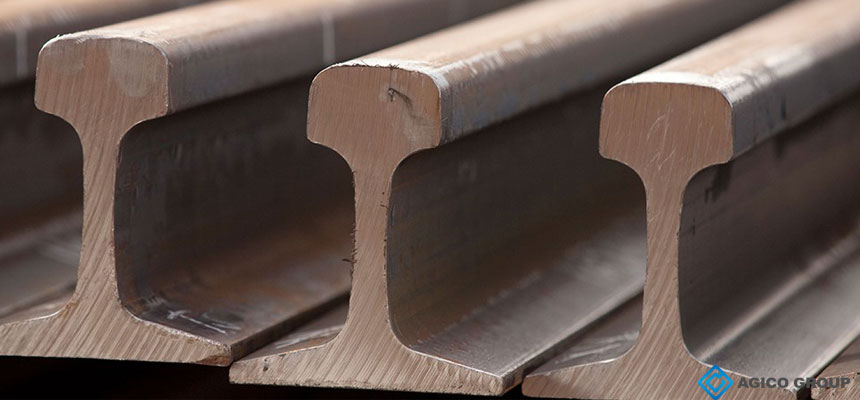
Get close to steel rail
Steel rail types
Steel rail types are customarily expressed in kilograms (kg/m) of the mass per meter of rail. China's rail standard include 75kg/m, 60kg/m, 50kg/m, 43kg/m, 38kg/m, etc. in the international market, there are AREMA, BS, JIS, UIC, DIN and other standard rail.
The type of rail should be adapted to the volume, allowable speed and axle weight. The selection of rail type should be considered based on the transport conditions. Technically, it is necessary to ensure sufficient strength, toughness, wear resistance and stability; economically, ensure a reasonable overhaul cycle and reduce the maintenance. The main factors for determining the mass (weight) of the rail:
- Firstly, the rail quality must match the axle load of the locomotive, the axle ratio is generally above 2.75, and the rail quality is increased to match the axle load;
- Secondly, under the condition of certain speed, the impact of the wheel on the rail, the vibration of the rail components and the track bed is inversely proportional to the quality of the rail. To improve the speed of the train and ensure good quality of railway line, the quality of the rail must be improved.
- Thirdly, the greater the total mass passed, the more easily it causes the fatigue damage of the track components and the geometric transformation of the track. Therefore, it is necessary to select the matching rail according to the annual total quality, so as not to affect the service life of the rail and shorten the overhaul period of the line overhaul.
Shape and size of rail section
In a straight section, the force on the rail is primarily a vertical force, which results in deflection of the rail. Since the rail is considered to be an infinitely long beam supported on a continuous elastic foundation, the optimum cross-section of the beam against deflection is an I-shape. Therefore, the rail adopts an I-shaped section, which is composed of a rail head, a rail waist and a rail bottom. The rail section size should meet the following requirements:
The rail head is the part directly contacting the wheel. In order to improve the contact condition of the wheel and rail, and improve its resistance to indentation and wear resistance, the rail head should be large and thick, and it should have a tread surface, and adapted shape and sufficient area for wear;
- To make the rail have greater bearing capacity and bending resistance, the rail waist must have sufficient thickness and height, and the sides of rail waist may be straight or curved. The curve is most commonly used;
- The bottom of the rail is directly supported on the top surface of the sleeper. For keeping the stability of rail, the bottom of the rail should have sufficient thickness and width, and have the necessary rigidity and resistance to corrosion.
- The head top width (b), rail waist thickness (t), rail height (H) and rail bottom width (B) of the rail are the four main parameters of the rail. Their area allocation should be considered according to various aspects. Choose the most appropriate ratio.
Rail damage standard
Rail damage refers to rail breakage, rail cracks, and other damage that affects and limits the performance of the rail during use. Rail damage is classified into three categories: light injury, serious injury and fracture.Rail breakage refers to one of the following conditions:
- The full section of the rail is broken;
- The crack penetrates the entire rail head section;
- The crack penetrates the entire rail bottom section;
- The allowable speed is not more than 160km/h. The top surface of the section rail has a block with a length greater than 50mm and a depth greater than 10mm.
- The allowable speed is greater than 160km/h. The top surface of the section rail has a block with a length greater than 30mm and a depth greater than 5mm.
- Rail Fasteners
- rail fastening system
- rail clip
- railroad spike
- Track bolt
- rail shoulders
- rail anchor
- rail clamp
- tie plate
- Rail Pad
- rail insulator
- rail plastic dowel
- other rail fasteners
- Railway Switch
- SKL series rail fastening system
- Chinese standard rail fastening system
- screw spikes
- Crane rail fastening system
- K type rail clip for Africa
- Hey-Back Rail Fastening
- rail fasteners for Mexican market
- Ss25 screw spike
- Ss35 rail sleeper screw spike
- Ss8 screw spike
- coach screw
- Crane Rail Clip
- Rail Joints (Fishplate)
- Steel Rail
- Railway Sleeper
 rail clip
rail clip
 rail joints
rail joints

 Español
Español English
English

